Fresh forecasting and replenishment: Master weekday variation
Nov 28, 2024 • 8 min
Customer demands for fresh products can seem as unpredictable as the weather. That is, until you learn how to forecast for weekday variation.
One key challenge in achieving inventory balance is the significant variation in consumer demand across different days of the week—customers buy different products on Tuesdays and Saturdays.
These fluctuations can hurt your efforts to reduce waste if not accurately accounted for in your daily forecasting approach. But by effectively incorporating weekday variation into retail grocery forecasting for fresh foods, you can minimize waste, save money, and enhance your store’s sustainability.
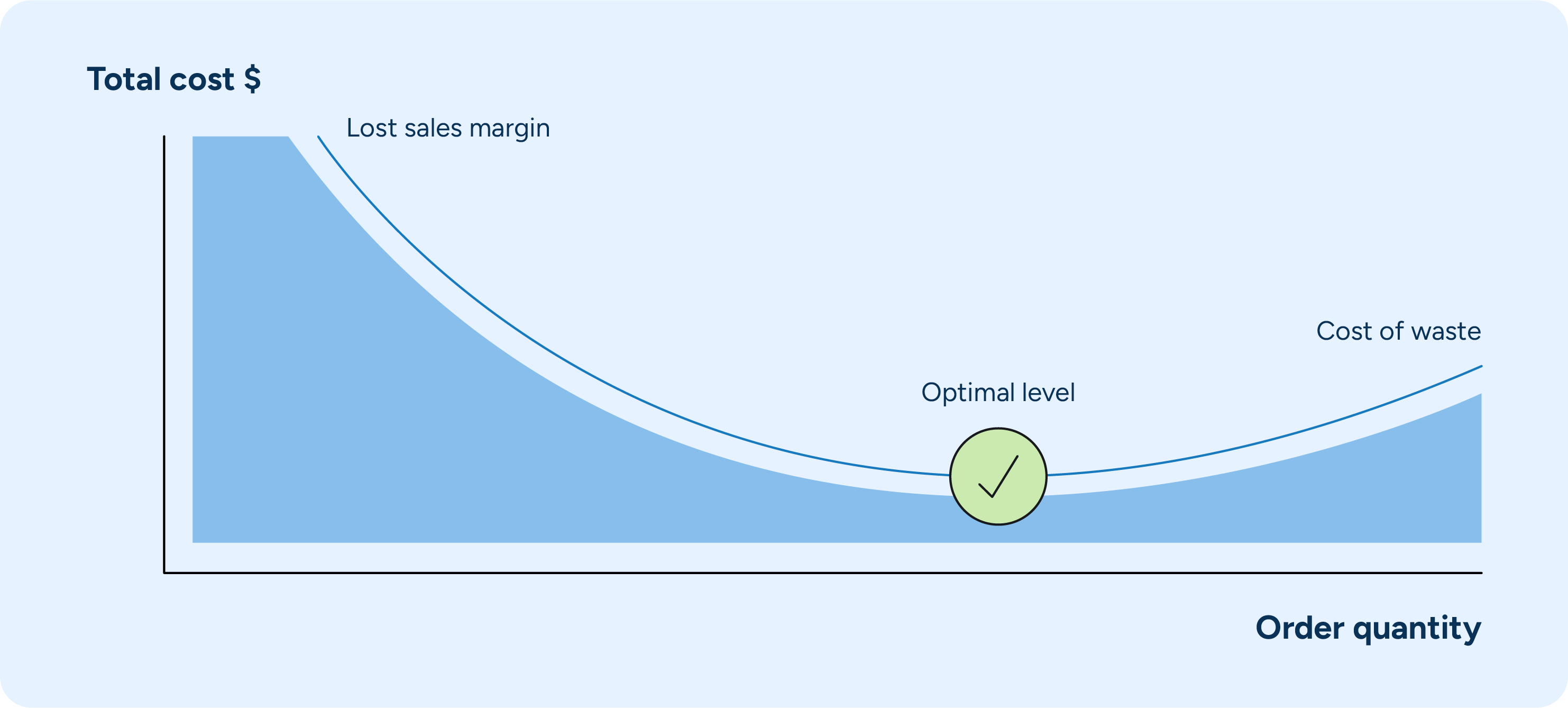
1. Analyze historical data
To effectively incorporate weekday variation into your forecasting, start by regularly analyzing historical sales and spoilage data. This analysis helps identify patterns and trends specific to different weekdays. By segmenting the data by individual days, such as Mondays, Tuesdays, and so on, you can gain a clearer understanding of how demand and spoilage vary throughout the week.
For instance, analyzing sales and spoilage data separately for each weekday allows you to pinpoint specific patterns. Use statistical methods and visualization tools to identify recurring trends. Look for consistent peaks or troughs in sales and spoilage rates on specific days. Weekends might show higher sales due to increased shopping activity, while mid-week might have lower demand. By examining these patterns, you can adjust your forecasts to better match actual demand.
It’s also important to examine long-term trends to see if certain days are becoming more or less significant over time. This can help you adjust your forecasts to account for evolving shopping behaviors.
Investigating and understanding correlations between various factors and sales or spoilage rates can further refine your forecasting accuracy. For example, promotions might significantly boost sales on certain days. At the same time, adverse weather conditions might lead to higher spoilage rates for perishable goods as customers are likely to avoid shopping during adverse weather.
By identifying these correlations, you can refine your inventory management to better match demand while reducing waste. This comprehensive approach enables you to make data-driven decisions that enhance both customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Finally, feeding segmented and analyzed data into machine learning models enhances their predictive accuracy. These models can learn from historical patterns and trends to forecast future demand and spoilage more accurately. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning, you can make more informed decisions and reduce spoilage, ultimately improving both economic efficiency and customer satisfaction.
2. Leverage machine learning
To enhance the accuracy of your forecasts, leverage machine learning (ML) techniques through a process known as feature engineering. This involves processing historical data to create features the ML model can use. By identifying patterns such as seasonality, day-of-week effects, and promotional impacts, you can provide the model with the necessary context to make more accurate predictions.
Once the features are engineered, the next step is model training. Advanced ML algorithms, such as time series models or neural networks, are trained on historical data. These models learn to predict future demand by recognizing complex patterns and relationships within the data. The training process allows the models to understand how different factors influence demand and spoilage, enabling them to make more informed predictions.
After training, the ML models generate forecasts at a granular level, such as product-SKU-day. This granularity allows retailers to predict demand for each product on a specific day, taking into account factors like promotions and weather. By generating detailed forecasts, retailers can better manage their inventory, reducing the risk of spoilage and ensuring that fresh products are available when customers need them.
Continuous improvement is a crucial aspect of ML forecasting. The models are continuously updated with new data to improve their accuracy. Retailers also monitor the forecasts’ performance and adjust the models as needed. This iterative process ensures the forecasts remain relevant and accurate, helping retailers stay ahead of changing demand patterns and minimize waste.
3. Implement day-specific forecasting
To effectively manage inventory and reduce spoilage, implement day-specific forecasting models that account for variations in demand across different days of the week. By tailoring replenishment plans to the specific demand patterns of each weekday, you can significantly reduce the risk of overstocking and spoilage. This approach ensures that your inventory levels align more closely with actual consumer behavior.
Integrating day-of-week adjustments into your forecasting models can capture these variations. For example, the model might predict higher demand on Fridays and Saturdays due to increased weekend shopping. By understanding these patterns, you can adjust your inventory levels accordingly, ensuring you have enough stock to meet demand without overstocking.
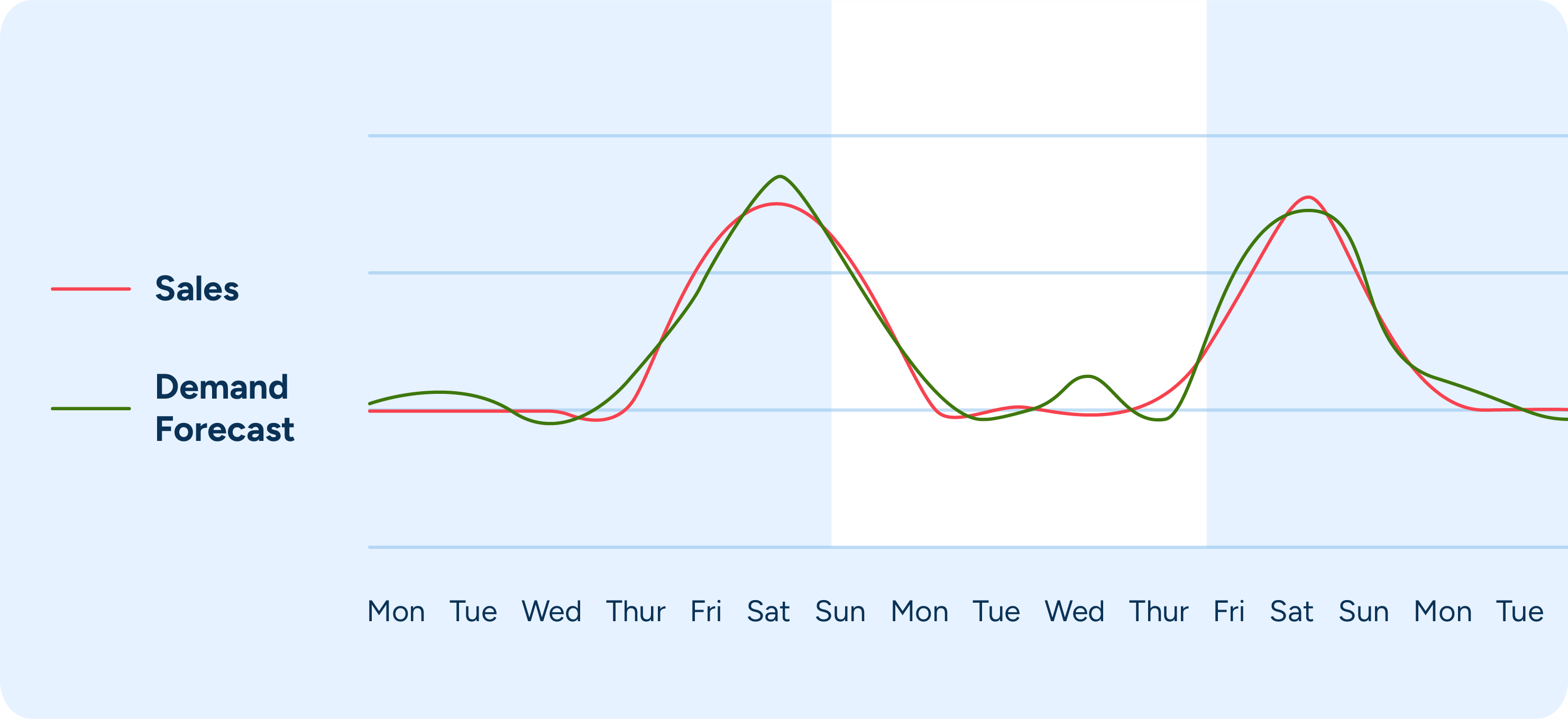
Dynamic inventory management practices are essential for adapting to the varying demand patterns throughout the week. Implementing practices that adjust orders and stock levels based on day-specific forecasts enables more responsive and flexible inventory control, helping you better manage stock and reduce waste.
Your day-specific forecasts will need regular monitoring to ensure accuracy and adjustment as necessary. This involves comparing forecasted demand with actual sales and refining the models to improve their predictive accuracy over time. By continuously evaluating and updating your forecasts, you can ensure that they remain accurate and relevant.
It’s also important to integrate other influencing factors, such as promotions, holidays, and weather conditions, into your day-specific forecasting models. This provides a more comprehensive view of demand and helps make more accurate predictions. By considering these additional factors, you can further enhance the precision of your forecasts and better meet your customers’ needs.
4. Monitor promotions and events
It’s crucial to monitor promotions and events closely to accurately forecast demand and reduce spoilage. By accurately modeling price elasticity and considering a product’s price position within its category, retailers can predict demand variations caused by business decisions like promotions and price changes.
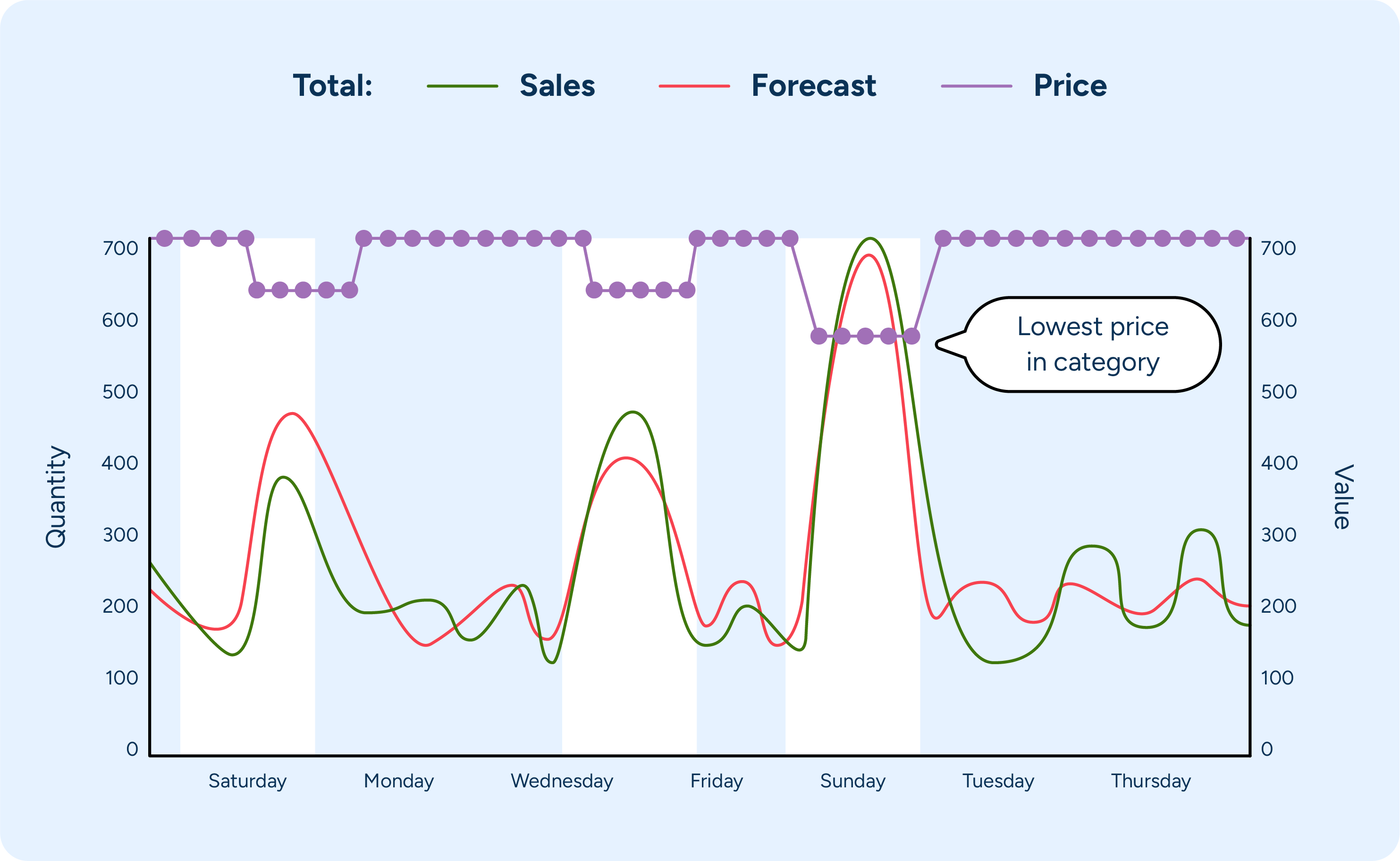
Maintaining a detailed record of all upcoming promotions, holidays, and local events that could impact demand is also essential. This includes national holidays, local festivals, store-specific promotions, and marketing campaigns. By maintaining a comprehensive calendar of these events, you can better anticipate changes in consumer behavior.
By reviewing historical data, you can get insight into how similar promotions and events have affected demand in the past. Identifying patterns such as increased sales during holiday seasons or specific promotional periods allows you to predict how upcoming events might influence demand and adjust your forecasts accordingly.

From there, the expected impact of these promotions and events can be incorporated into your forecasting models. You can then adjust the day-specific forecast for anticipated demand spikes or drops. For example, increased forecasted demand for products on days when a major promotion is running will likely mean competitor brands of similar products see reduced demand. Knowing this, you’ll likely need to stock less of the competing products during promotions to ensure sufficient stock to meet demand without overstocking.
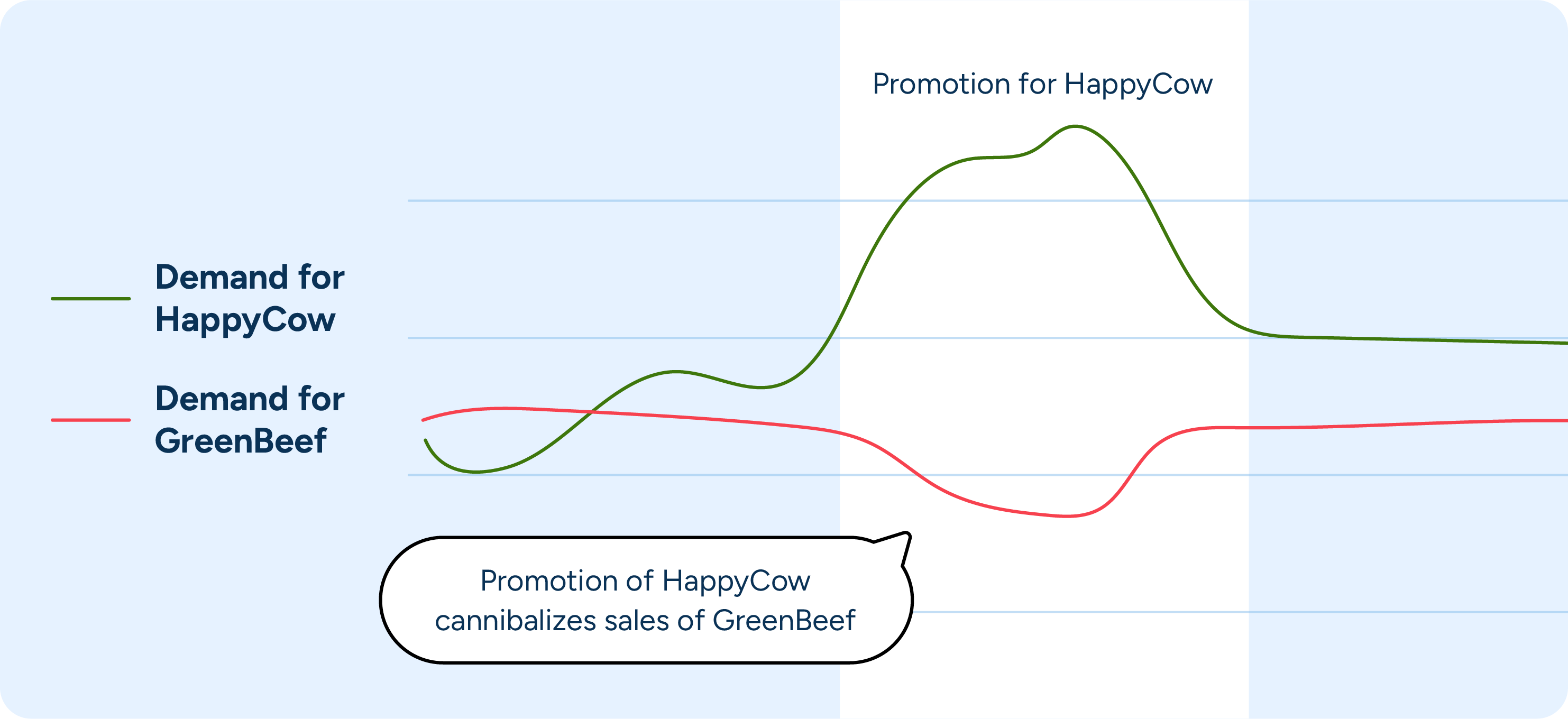
As sales come in during the event or promotion, you can continuously monitor data in real-time during promotions. This allows for quick adjustments to replenishment plans if actual demand deviates from the forecast. For instance, if a promotion is more successful than anticipated, additional stock can be ordered promptly to avoid stockouts. Real-time monitoring ensures that your inventory levels remain optimal throughout the promotional period.
After the promotion or event, you’ll have actual sales and spoilage data to evaluate the forecasts’ accuracy and the inventory adjustments’ effectiveness. You can use these insights to refine future forecasting and inventory management strategies. By learning from each event, you can continuously improve your forecasting accuracy and reduce spoilage, ultimately enhancing both economic efficiency and customer satisfaction.
5. Optimize delivery schedules
Another way to reduce spoilage and maintain product freshness is coordinating with suppliers to optimize delivery schedules based on weekday demand variations. Implementing more frequent deliveries of smaller quantities, particularly for perishable items, helps ensure that stock levels remain optimal and products are replenished regularly. This approach minimizes the risk of spoilage by keeping inventory fresh and aligned with actual demand.
Based on the day-specific demand forecasts, you can adjust the frequency of deliveries to match the expected sales. For example, schedule more frequent produce deliveries on high-demand days and fewer on low-demand days. This approach, called delivery smoothing, ensures that you have the right amount of stock when you need it, reducing both overstock and stockouts.
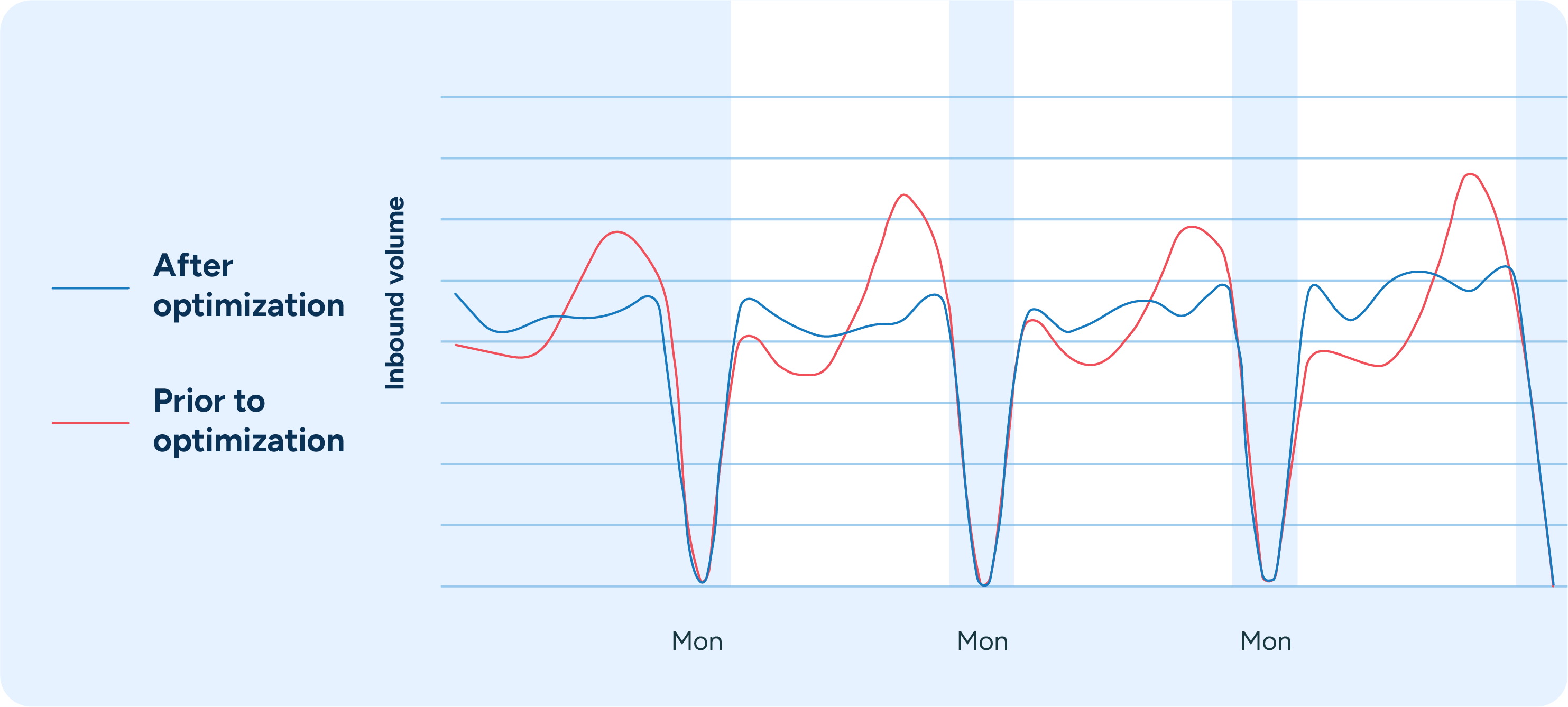
Working closely with logistics partners to ensure that the delivery schedules are feasible and cost-effective will help optimize routes and delivery times, further enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. By continuously evaluating and refining your delivery schedules, you can maintain a high level of service while minimizing waste.
Additionally, incorporating minimum order quantities (MOQs) into your fresh ordering processes ensures that orders are optimized despite MOQs. This consideration helps balance the need for frequent deliveries with the practical constraints of ordering and logistics. Integrating MOQs into your delivery planning allows you to maintain efficiency and cost-effectiveness while still meeting demand.
Forecasting a more sustainable future
The importance of sustainability in grocery retail will only continue to grow. To stay ahead of the competition, it’s crucial to leverage cutting-edge technology and specialized AI to predict consumer demands more precisely. By continuously refining your forecasting models and incorporating advanced analytics, you can not only reduce spoilage but also contribute to a more sustainable food system.
It’s vital to embrace these innovations and stay committed to using data-driven insights to optimize your inventory management. A proactive approach will help you meet customer needs efficiently while simultaneously minimizing environmental impact, raising the bar on profitability and sustainability.



