Production scheduling: Nitty-gritty planning for big picture benefits
Oct 30, 2024 • 11 min
Production scheduling is the key to hitting production targets strategically – neither underutilizing resources nor attempting impossible targets with resources you don’t have; not overreacting to fluctuations but adapting in time to avoid costly delays.
The production environment is an entire nervous system of constraints – lead times, availability, capacity, resource allocation, labor, and more. It’s up to planners to coordinate these moving parts, keeping production on track and aligned with business targets. It’s a delicate balance, and the right production scheduling technology helps planners maintain it.
Production scheduling works like supply chain hand-eye coordination. Visibility into data from across the network helps planners assess the impacts of constant supply and demand changes and make production decisions that guarantee delivery in the most cost-effective way.
What is production scheduling?
Production scheduling determines the sequence and timing of production tasks to best use available resources while ensuring timely delivery.
Optimal production scheduling solutions consider material availability and ship dates, as well as delivery times, sequences, allergens, tools, packaging, and any other factor integral to the production process. Based on this information, they create plans that can be easily reviewed and adjusted based on available labor and resources to improve service levels and minimize delays.
Production scheduling vs production planning
Production scheduling is a subset of production planning.
Production planning sets targets, determining what, where, and how much to produce in daily or weekly buckets, supporting both operational and tactical planning. The production targets are based on the expected demand and forecasts for each location.
Production scheduling breaks that plan down, allocating and sequencing production activities down to the minute and second. It details when and where each activity must be executed.
For the example below, an ice cream manufacturer’s production plan outlines a target of 10,000 units of vanilla ice cream for the week. The production schedule takes that target and determines the time and work center at which each step of production will take place.
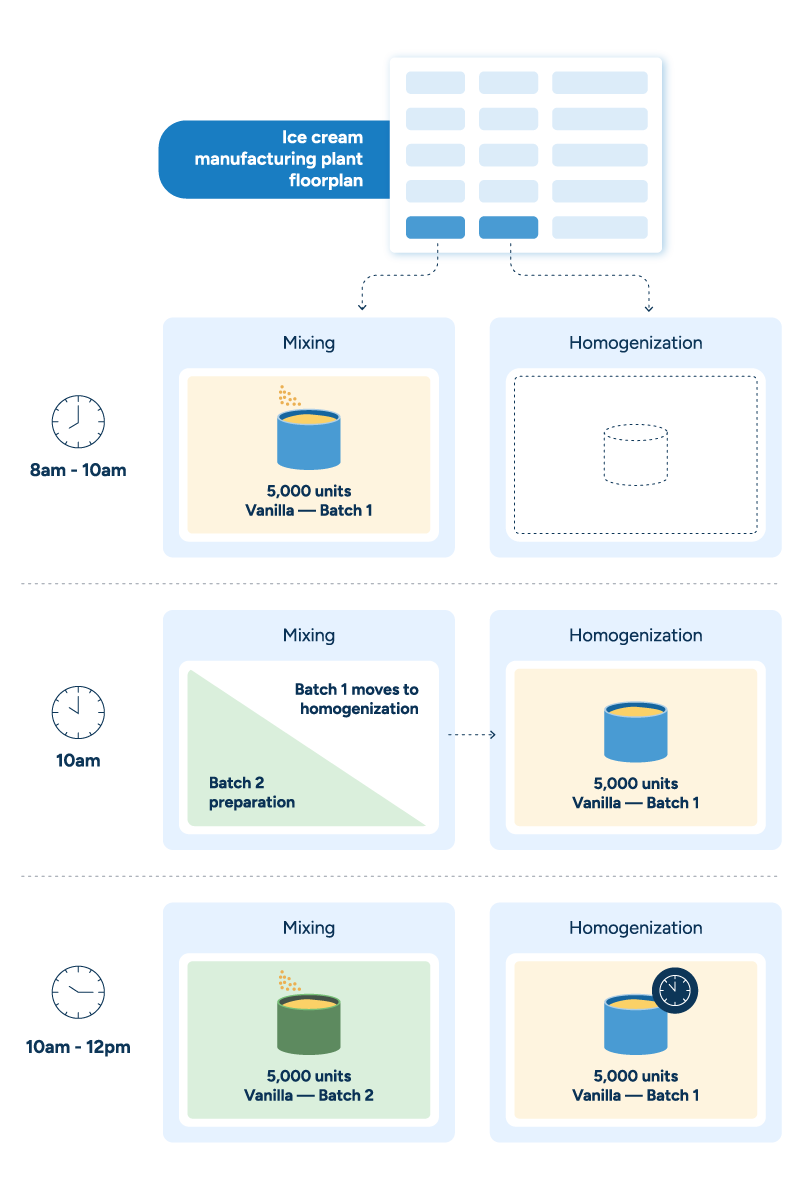
The production plan directs the schedule by setting overall objectives. The production schedule figures out how best to achieve those targets.
Read more: Production planning without the headaches
The importance of production scheduling
The impact of production scheduling and its role in an organization comes down to granularity.
For some businesses, having a weekly overall production plan that outlines what, where, and how much to produce will be enough. A few minor tweaks and perhaps some manually created sequences provide all the necessary data to send to the floor for execution.
However, the more complex the manufacturing process becomes, the more a production schedule that organizes the various moving components and makes the best use of available time, labor, and resources becomes necessary.
The benefits of automated production scheduling
Production scheduling is not just about the factory floor. The benefits of an optimized production schedule begin with the planners, weave their way through execution, and land in the board room.
There are efficiency and productivity gains that can significantly widen company margins. By minimizing the total cost for production and maximizing production efficiency, inventory costs themselves are reduced. On the other end of the supply chain, better product availability means happier customers and increased sales. Lower costs, more sales, higher profit.
Faster, smarter responses to market shifts
Optimized production scheduling usually involves a departure from once-ubiquitous spreadsheets. Spreadsheets typically require manual input and aren’t built to balance all the constraints and business rules inherent in a complex production environment. They rely on manual input, gut feeling, and planners having a lot of time on their hands…which they usually don’t.
Automated planning solutions drastically shorten the time required to generate schedules, allowing teams to initiate smart, rapid responses to changes in supply, demand, and capacity. They balance constraints and requirements to design an optimal plan that maximizes delivery service at the lowest cost.
Increased planning efficiency and flexibility
Automated production scheduling solutions ensure finite schedules are fully aligned with higher-level production plans, cutting down on waste and confusion. They increase resource utilization by helping planners understand future needs and material availability and alerting them to future shortages. Automation also helps minimize set-up and cleaning time to increase production efficiency and reduce overtime.
Some companies use their solution for medium-term decisions, simulating the outcomes of changes, such as increasing the number of shifts to meet production targets, before putting those changes into effect.
Better visibility and collaboration
Production scheduling software provides clear visibility across the organization. Each team is looking at the same dataset and plan, increasing trust in the automated recommendations and minimizing the time wasted debating options or collecting information.
This shared view also eliminates the possibility of having multiple versions of the truth confusing plans and operations. Spreadsheets can take on a life of their own, growing more unruly as teams change them to fit smaller, bespoke needs without being able to communicate those changes easily across the business. By providing one source of truth with a network-wide view across planning functions, automated systems eliminate the need for version control.
Better OTIF rates and increased service levels
With more forward visibility, the entire planning team understands what can and cannot be delivered. This information helps teams set and manage market expectations. Being able to fine-tune the production plan means they can maximize delivery service, avoiding the tendency to produce some orders too early and others too late. This increases the on-time, in-full (OTIF) rates while keeping service levels high.
More time-efficient processes
Optimized production schedules ensure the right production activities happen at the right time in the right order. By reducing the amount of stopping and starting between these tasks, these plans support longer production runs, sequencing items to reduce downtime on the line. One simple example would be ensuring that allergens are introduced after tasks that need to be allergen-free have been completed, minimizing necessary cleaning.
Production scheduling challenges
When it comes to production scheduling, manufacturers face challenges both internal and external.
Managing multiple constraints
Production environments are rife with complexity. Planners must balance machine capacities, labor availability, set-up, and maintenance, calibrating precise quantities and timing to minimize costs and inefficiencies. It’s a delicate balance and not an easy one to strike manually.
Food manufacturers also need to contend with cross-contamination and allergens, which can make sequencing and cleaning more difficult.
Fluctuating environments
With so many moving parts and so many contributing factors, plans can be pulled drastically off course. Sudden demand changes and supply chain disruptions can cause bottlenecks, stockouts, and any number of scheduling headaches. Plus, even in the most well-maintained factories, machines need oiling, belts break, and equipment fails. These disruptions and setbacks have immediate ramifications and require real-time production schedule adjustments.
Poor data integration
The most detailed production schedule in the world won’t help much if it’s built on poor data.
Production planners receive data from every direction—from inventory levels and order forecasts to lead times and supplier constraints. Spreadsheets and legacy planning solutions aren’t built to organize, integrate, and analyze this data from across the supply chain.
What’s more, many planners have tons of legacy knowledge (of varying import and accuracy) in their heads that never finds a place in their planning systems. Without an automated solution, it’s nearly impossible to systematize this legacy knowledge and generate actionable insights from it with minimal manual input.
Siloed planning
Production scheduling should not be isolated. It plays an integral role in the supply chain and must be able to communicate and coordinate easily with other departments.
In an ideal world, updates to the schedule should constantly feed back into the planning process to generate new plans. For instance, if an order is completed sooner than expected, a new order can take its place. On the other hand, if an order has been delayed, the plan should be adjusted to compensate for that instead of bombarding the production floor with orders it cannot fulfill in time.
Manual and spreadsheet-based planning processes, however, don’t offer the visibility and collaboration needed for informed production decisions. This lack of integration isn’t just between different planning functions. Often, planners at different plants throughout a company end up with vastly different, locally created spreadsheets. Without shared data and workflows, planners cannot react to the latest ERP information quickly enough to align operations across the organization.
Essential software features for optimized production scheduling
A production scheduling solution first requires automation. Backed by automation, planners can focus on exception management, respond more quickly to changes, and make better, data-driven decisions.
Here are the six hallmarks of ROI-driving production scheduling software.
1. Automatic production schedule generation
The solution creates a detailed schedule broken down by the hour, minute, and second, setting and managing penalties to guide scheduling without manual intervention. It ensures those schedules adhere to predefined rules and use real-time data. This means planners can rapidly generate new schedules as changes occur while reducing errors, improving utilization, and meeting demand.
2. Automatic order sequencing
An automated solution can sequence tasks according to given constraints and factors such as product type, allergens, priority, due dates, and resource availability. This keeps production lines running smoothly and efficiently with minimal downtime, helping companies meet delivery deadlines consistently, increasing service levels, and improving brand reputation.
3. Automatic order visualization and synchronization
Production scheduling software gives planners shared workflows and more centralized processes, so they can communicate and collaborate more effectively.
Order visualization provides a clear, graphical representation of the planned production schedule so planners can more easily monitor progress and head off any impending issues.
Order synchronization means that production orders are updated in real time across all supply chain functions, so every team is working with the same information.
These automated tools allow planners to make better decisions and communicate those decisions quickly across the organization, ensuring that the production process continues smoothly and stays aligned with overall goals.
4. Automated scarcity prioritization
Not all customer orders are created equal; some are more urgent or hold more strategic importance than others.
Using an optimized penalty matrix that outlines inventory and demand requirements by SKU-site, the solution’s algorithms can produce priority orders first when faced with scarce production capacity. This helps companies maintain service levels, reduce stockout risks for high-priority items, and optimize overall efficiency.
5. Scenario planning
The solution should have mathematical optimization capabilities that allow it to balance multiple constraints and run scenarios within a digital twin. This allows planners to test the outcomes of decisions before putting them into action.
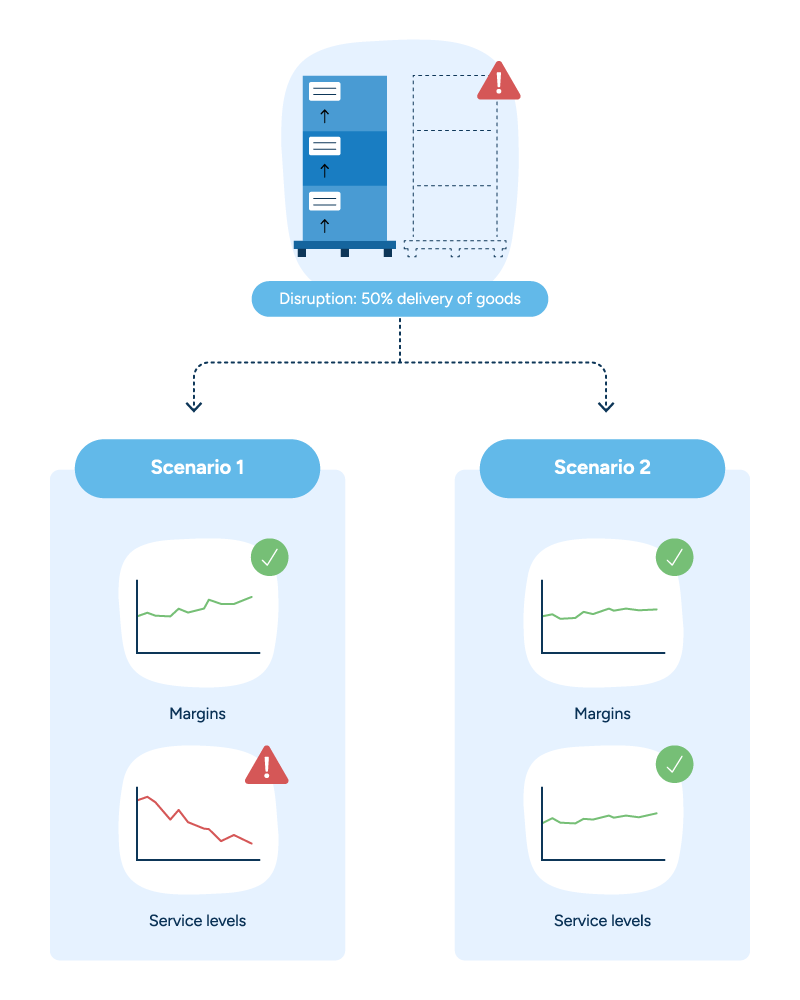
For instance, suppose a new demand pattern crops up, a shipment arrives late, or a production line breaks down. Events like these will have an immediate impact on production needs and operations. A planner can use the digital twin to test how a certain response would affect the production schedule and trace the ripple effects throughout the supply chain to determine the best course of action.
READ MORE: Vita Coco streamlines operations with optimization and digital twins
6. Seamless integration with production planning
Production scheduling sits inside production planning. By integrating the two processes and allowing easy, two-way data sharing, companies ensure schedules are based on current plans and forecasts. With better coordination, teams spend less time manually trying to fix problems that spreadsheets can’t solve and more time improving efficiency and aligning production with customer demand and overall business objectives.
How RELEX production scheduling drives business benefits
RELEX has deployed production scheduling as part of a comprehensive planning solution at companies worldwide.
For instance, Tegel Foods uses RELEX to generate demand forecasts and weekly production plans for the entire business. Each production facility maintains control of the production scheduling, allowing for more local control of detailed day-to-day operations while aligning with company-wide objectives and processes. By incorporating scheduling into overall supply chain planning, the company has improved the S&OP process, increased forecast accuracy and production throughput, and reduced inventory and waste.
“RELEX is a tool that allows us to run the business better. If you consistently make better business decisions, the financial side will take care of itself. In our case, it certainly has.”
Arijit Saha, General Manager of Supply Chain at Tegel
Another customer with impressive success is Finsbury Food Group, one of the UK’s leading specialty bakery manufacturers. Again, production scheduling was woven into an entire supply chain solution. As part of this cohesive planning system, Finsbury implemented production scheduling optimization at each of its production sites. Using the first weeks of their production plan, the tool helped schedulers determine optimal production sequences, factoring in capacity, labor constraints, sequencing rules, and available materials. This integrated solution is both driving ROI and paving the way for better processes across the business. Finsbury reduced net working capital by £1.6 million and improved service levels in Food Services by 5% year-on-year.
The role of production scheduling in a comprehensive planning solution
Production scheduling provides the nitty-gritty plan that keeps production activities on track and on time. The levels of granularity and coordination ensure high-performance production, even in the most complex manufacturing environments.
But it’s important to remember that production scheduling contributes and depends on an advanced planning and scheduling solution that takes advantage of data and AI-driven insights from across the network, helping businesses establish themselves as reliable supply chain partners, stay profitable and flexible amid market volatility, and deliver on promises to customers.



